What is Serialization in Java?
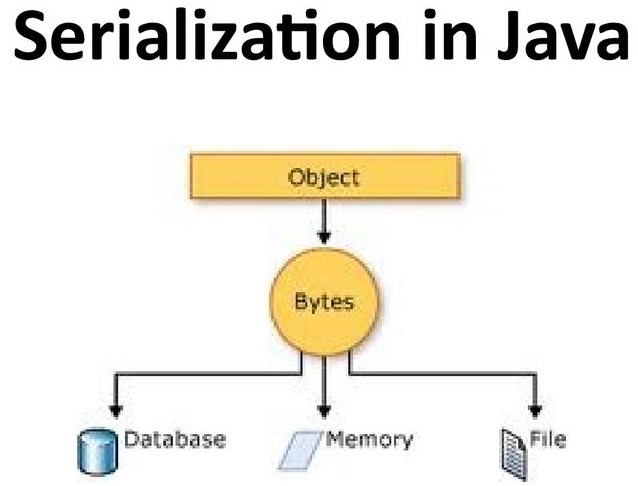
Object Serialization in Java is a process used to convert Object into a binary format which can be persisted into disk or sent over network to any other running Java virtual machine; the reverse process of creating object from binary stream is called deserialization in Java.
Java provides Serialization API for serializing and deserializing object which includes java.io.Serializable, java.io.Externalizable ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream etc.
Java programmers are free to use default Serialization mechanism which Java uses based upon structure of class but they are also free to use there own custom binary format, which is often advised as Serialization best practice, Because serialized binary format becomes part of Class’s exported API and it can potentially break Encapsulation in Java provided by private and package-private fields.
Classes ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream are high-level streams that contain the methods for serializing and deserializing an object.
The ObjectOutputStream class contains many write methods for writing various data types, but one method in particular stands out:
Public final void writeObject(Object x) throwsIOException
The above method serializes an Object and sends it to the output stream. Similarly, the ObjectInputStream class contains the following method for deserializing an object:
public final Object readObject() throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException
This method retrieves the next Object out of the stream and deserializes it.
The return value is Object, so you will need to cast it to its appropriate data type.
The above explanation briefly defines and explains serialization.